Melanoma Detection Using Convolutional Neural Networks: A Deep Learning Approach
Introduction
Introduction: Skin cancer, particularly melanoma, is a significant health concern worldwide. Early detection is crucial for successful treatment.
Outline: This project leverages the power of Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) to automatically detect melanoma from skin lesion images, potentially assisting dermatologists in early diagnosis.
Dataset Overview: The dataset comprises 2357 images of various skin cancer types, including melanoma. These images are divided into 9 categories, representing different skin conditions. The data is split into training and testing sets, allowing for model validation.
My Approach
Data Preprocessing and Exploratory Data Analysis
Utilized Keras preprocessing for image standardization and normalization.
Visualized the distribution of images across different classes, revealing a significant class imbalance.
Plotted sample images from each category to understand the visual characteristics of different skin conditions.
Initial Model Architecture Designed a CNN with the following structure:
Multiple convolutional layers with ReLU activation
Max pooling layers for spatial dimension reduction
Flatten layer to transition from convolutional to dense layers
Dense layers with dropout for classification
Softmax output layer for multi-class classification
Identifying and Addressing over-fitting of data
Model Training and Evaluation
Trained the initial model for 20 epochs with a batch size of 32.
Implemented early stopping with a patience of 3 epochs, monitoring validation loss to prevent overfitting.
Initial model showed signs of overfitting, with training accuracy significantly higher than validation accuracy.
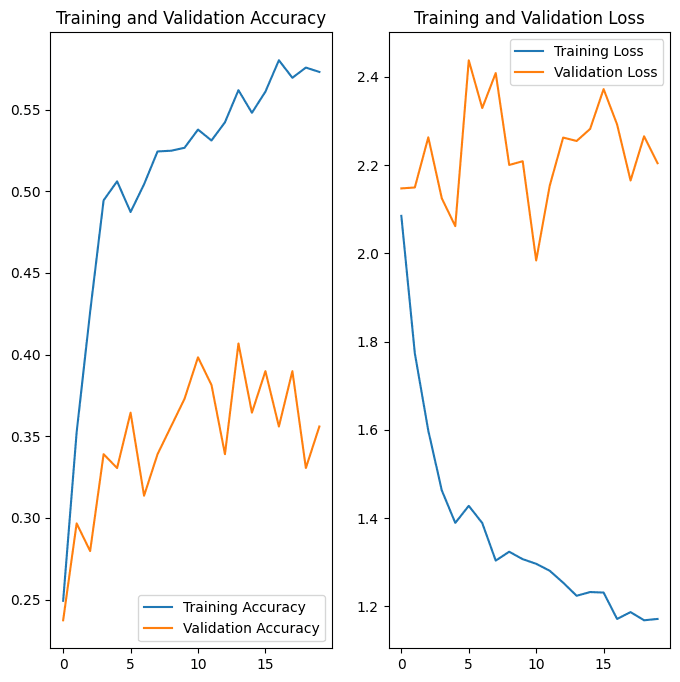
Addressing Challenges:
Data Augmentation - Implemented data augmentation using the Augmentor library.
Applied techniques including rotation, flipping, and slight color jittering.
This increased the diversity of the training set and helped address class imbalance.
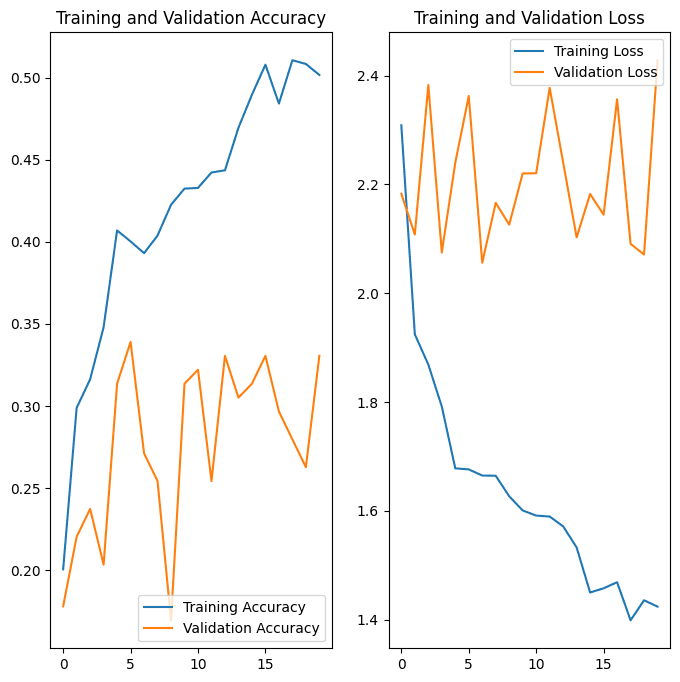
Plotted training vs. validation error to visualize overfitting.
Added dropout layers (0.5 rate) after dense layers.
Implemented L2 regularization in convolutional layers.
Experimented with different pooling strategies (max pooling vs. average pooling).
Normalized pixel values to the range [0, 1]. - Adjusted learning rate and implemented learning rate decay.
Final Model Performance
Achieved a final test accuracy of x%
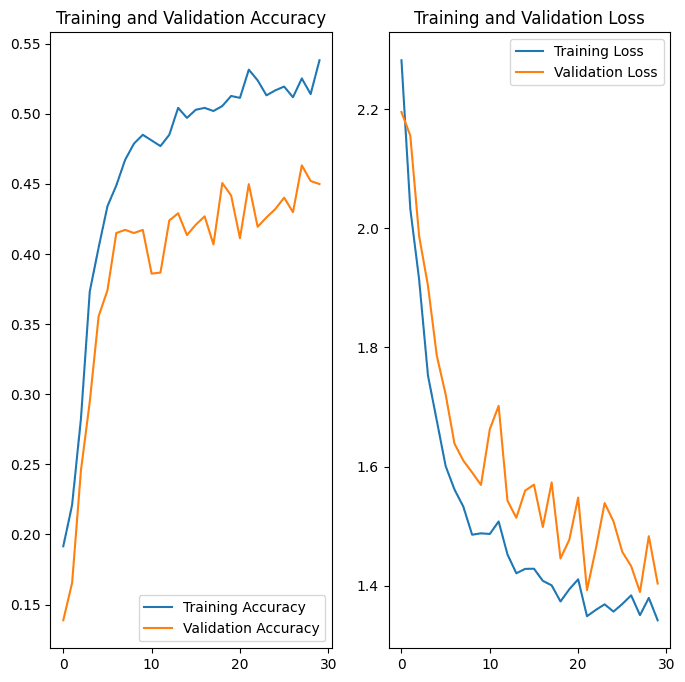
Significant improvement from the initial model's performance.
Presented a confusion matrix to visualize per-class performance.
Plotted ROC curves for each class to show model discrimination ability.
Conclusion and Future Work
The optimized CNN model demonstrates strong potential for melanoma detection.
Data augmentation and regularization techniques were crucial in improving model performance.
Future work could include:
Experimenting with more advanced architectures (e.g., ResNet, EfficientNet)
Incorporating additional data sources or metadata
Exploring interpretability techniques to understand model decisions
Technical Skills Demonstrated
Deep learning: TensorFlow and Keras for model building and training
Data preprocessing: Keras preprocessing, custom data augmentation pipelines
Model optimization: Hyperparameter tuning, regularization techniques
Data visualization: Matplotlib and Seaborn for performance and error analysis
Ethical Considerations and Real-World Application
Discussed the importance of model interpretability in healthcare applications.
Emphasized that the model should be used as a supportive tool for dermatologists, not as a replacement.
Highlighted the need for diverse and representative datasets in medical AI to ensure fairness and accuracy across different demographics.