Predicting User Engagement Scores in a Learning Management Platform
As a Data Analyst at a leading educational technology company, I undertook a project to develop an advanced machine learning solution for predicting user engagement in our Learning Management System (LMS). This project aimed to enhance user experience and improve content delivery by leveraging data-driven insights.
The Challenge:
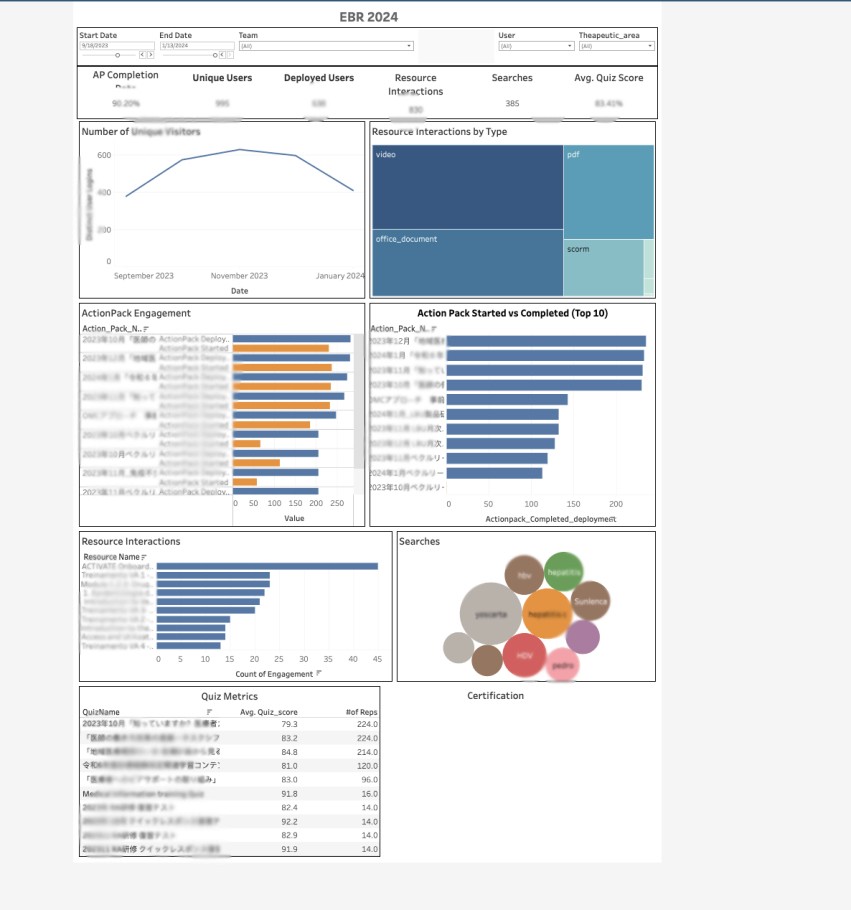
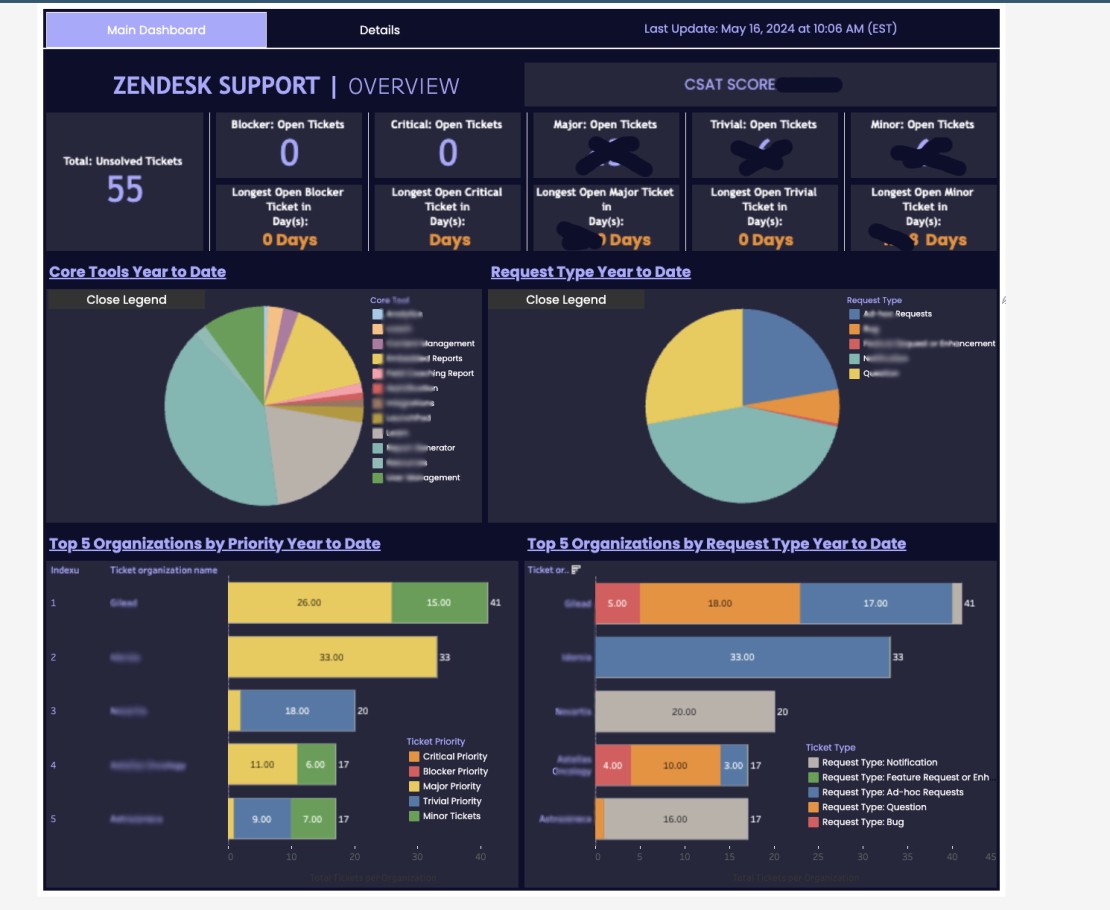
Our LMS serves thousands of users, generating vast amounts of interaction data. The primary challenge was to accurately predict user engagement levels in a multi-class setting, using a dataset of approximately 20,000 rows. Initial attempts at modeling this complex behavior yielded suboptimal results, with only a 35% F1-score.
My Approach:
Here are the steps I took to structure the data, and then perform training and validation to train a model to predict user engagement scores:
Data Preprocessing and Feature Engineering:
Cleaned and prepared the dataset, handling missing values and encoding categorical variables.
Created new features to capture user behavior patterns, such as total time spent on different activities and engagement ratios.
Implemented advanced techniques to handle temporal aspects of user interactions.
Addressing Class Imbalance:
Utilized the Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique (SMOTE) to balance our dataset, ensuring robust model performance across all engagement levels.
Model Selection and Development:
After evaluating several algorithms, we chose XGBoost for its ability to handle complex, non-linear relationships in data.
Implemented a rigorous cross-validation strategy to ensure model generalizability.
Fine-tuned hyperparameters using grid search with cross-validation to optimize model performance.
Feature Importance Analysis:

Leveraged XGBoost's built-in feature importance metrics to identify key predictors of user engagement.
This analysis provided valuable insights for product development and content strategy teams.
Results and Impact:
Significantly improved model performance, increasing the F1-score from 35% to 60%.
Achieved an impressive 86% ROC-AUC score in our 5-class prediction problem.
The enhanced predictive capabilities allowed for:
Personalized content recommendations, improving user satisfaction.
Early identification of at-risk users, enabling timely interventions.
Optimization of the overall learning experience on our platform.
Challenges Overcome:
Dealing with the complexity of multi-class classification in user behavior prediction.
Balancing model complexity with interpretability to provide actionable insights.
Integrating the model predictions into the existing LMS infrastructure for real-time user engagement enhancement.
Key Learnings:
The importance of feature engineering in capturing complex user behaviors.
The effectiveness of ensemble methods like XGBoost in handling diverse and noisy datasets.
The value of combining data science expertise with domain knowledge in educational technology.
Conclusion:
This project demonstrates my ability to develop end-to-end machine learning solutions that directly impact business outcomes and user experiences.
By leveraging advanced techniques in data preprocessing, feature engineering, and state-of-the-art algorithms like XGBoost, I significantly improved our ability to understand and predict user engagement in our Learning Management System.
This work not only enhanced our product offering but also contributed to our mission of providing personalized and effective learning experiences!